Your first SERP provider
Here we'll develop a SERP provider that performs math operations with 2 numbers.
Before we start
To develop SERP providers you need:
- Android Studio
- Android SDK platform, API 33 (13) (can be installed from Android Studio)
- A GitLab account
- Some knowledge of Kotlin
Setting up
- Fork Gugal.
- Clone your fork and open it in Android Studio.
- Make a package in the
com.porg.gugal.providerspackage calledcalculator.
Getting started
- Make a new Kotlin class in the package, called Calculator.
Add these import statements in the start of the class:
import com.porg.gugal.R import com.porg.gugal.data.Result import com.porg.gugal.providers.ProviderInfo import com.porg.gugal.providers.SerpProvider import com.porg.gugal.providers.responses.*These import Gugal's resources, the classes we talked about in the Theory section and all error responses.
Make your class implement
SerpProvider:class Calculator: SerpProviderIn
strings.xml, add these strings. The strings can be added to other translation files, but can be left untranslated.<!-- Calculator SERP provider strings --> <string name="serp_calc_title">Calculator</string> <string name="serp_calc_desc">Calculates things.</string>In the
Calculatorclass, add the following lines:companion object { val id: String = "366e0fd4acec4326b829216e2caf847f-calc" val providerInfo = ProviderInfo(R.string.serp_calc_title, R.string.serp_calc_desc, R.string.serp_calc_title, false) } // Information about this provider, like the name and description. override val providerInfo: ProviderInfo? get() = Companion.providerInfo
This adds a companion object to your class, with 2 variables containing the internal UUID and the user-visible provider information discussed in the section above.
In
ProviderInfo, arguments 1 and 2 set the provider's name and description in the setup wizard respectively, argument 3 sets the name in the app's search query field and argument 4 defines if this provider needs to be set up.At this point your
Calculatorclass should look like this.
Declaring your SERP provider to Gugal
Open
com.porg.gugal.setup.SetupSelectSerpActivity. FindgetInfoand add your provider there:else if (serpID == Calculator.id) return Calculator.providerInfoThe function should look like this:
private fun getInfo(serpID: String): ProviderInfo? { if (serpID == GoogleCseSerp.id) return GoogleCseSerp.providerInfo else if (serpID == SearXSerp.id) return SearXSerp.providerInfo else if (serpID == Calculator.id) return Calculator.providerInfo // Check if serpID matches your SERP provider's ID, and if so return your SERP provider's // provider info. return null }Open
com.porg.gugal.Globaland add your SERP provider toallSerpProvidersandsetSerpProvider:val allSerpProviders: Array<String> = arrayOf( GoogleCseSerp.id, SearXSerp.id, // ... Calculator.id ) // and in getInfo... else if (serpID == Calculator.id) serpProvider = Calculator()The function should look like this:
fun setSerpProvider(serpID: String) { if (serpID == GoogleCseSerp.id) serpProvider = GoogleCseSerp() else if (serpID == SearXSerp.id) serpProvider = SearXSerp() else if (serpID == Calculator.id) serpProvider = Calculator() // Check if serpID matches your SERP provider's ID, and if so set Global.serpProvider to // an instance of your SERP provider. }setSerpProviderselects the SERP provider based on the ID, andgetInforeturns its info.Build and install Gugal. You might have to uninstall the existing app, and if you have already set up Gugal you will have to clear its data. These are destructive actions, so make sure you have a backup of either the app's data or your CSE credentials/SearX instance URL.
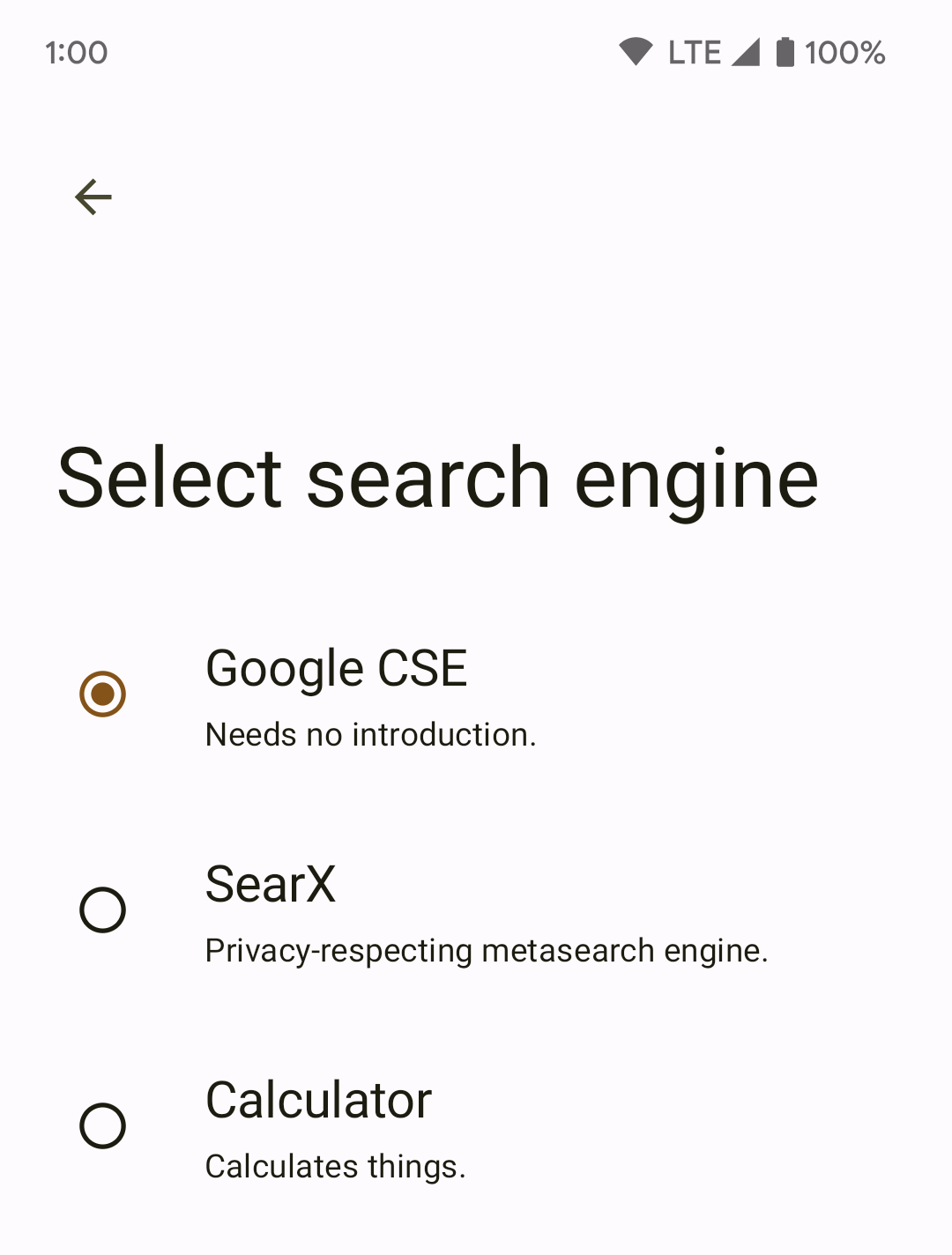
- Start set-up, and you should see your SERP provider:
Adding search-related methods
We are going to make a simple 2-number calculator.
Add a function for detecting the operation:
private fun getOperation(query: String): String { return when { query.contains("*") -> "*" query.contains("/") -> "/" query.contains("+") -> "+" query.contains("-") -> "-" else -> "?" } }This is a simple when expression that checks for math operations in the query and returns the operation, or ? if there is none.
Add a function for splitting the query into numbers:
private fun splitIntoNumbers(query: String): Array<Int> { val splitStrings = query.split("*","/","+","-") }This splits the string with math operations - multiplication, division, addition and subtraction - as delimiters. However, the function will give an error, because we aren't returning an array. Let's fix that.
Add these lines to the function:
val numArray: Array<Int> = Array(splitStrings.count()){ 0 } for ((index, str) in splitStrings.withIndex()) { numArray[index] = str.toInt() } return numArray
This part converts the numbers we found earlier into integers for math operations to work.
Line 1 makes an array of zeros with the same length as the number string array. Lines 2-4 define a for loop, which iterates over the number string array, converts the strings to integers and adds them to the array in line 1. Line 5 returns the finished array.
Your function should look like this:
private fun splitIntoNumbers(query: String): Array<Int> { val splitStrings = query.split("*","/","+","-") val numArray: Array<Int> = Array(splitStrings.count()){ 0 } for ((index, str) in splitStrings.withIndex()) { numArray[index] = str.toInt() } return numArray }And your
Calculatorclass should look like this.
Adding search
- Override
SerpProvider.searchin your class:override fun search(query: String, setResults: ((List<Result>) -> (Unit)), setError: ((ErrorResponse) -> (Unit))): JsonObjectRequest? {} - the user's query,
- a function for setting the search results,
- a function for sending an error response to the app.
The function can return a Volley JsonObjectRequest, which will be performed. Our SERP provider doesn't need this however.
In
search(), create a mutable list:val list: MutableList<Result> = mutableListOf()In the same function, add lines for calling the
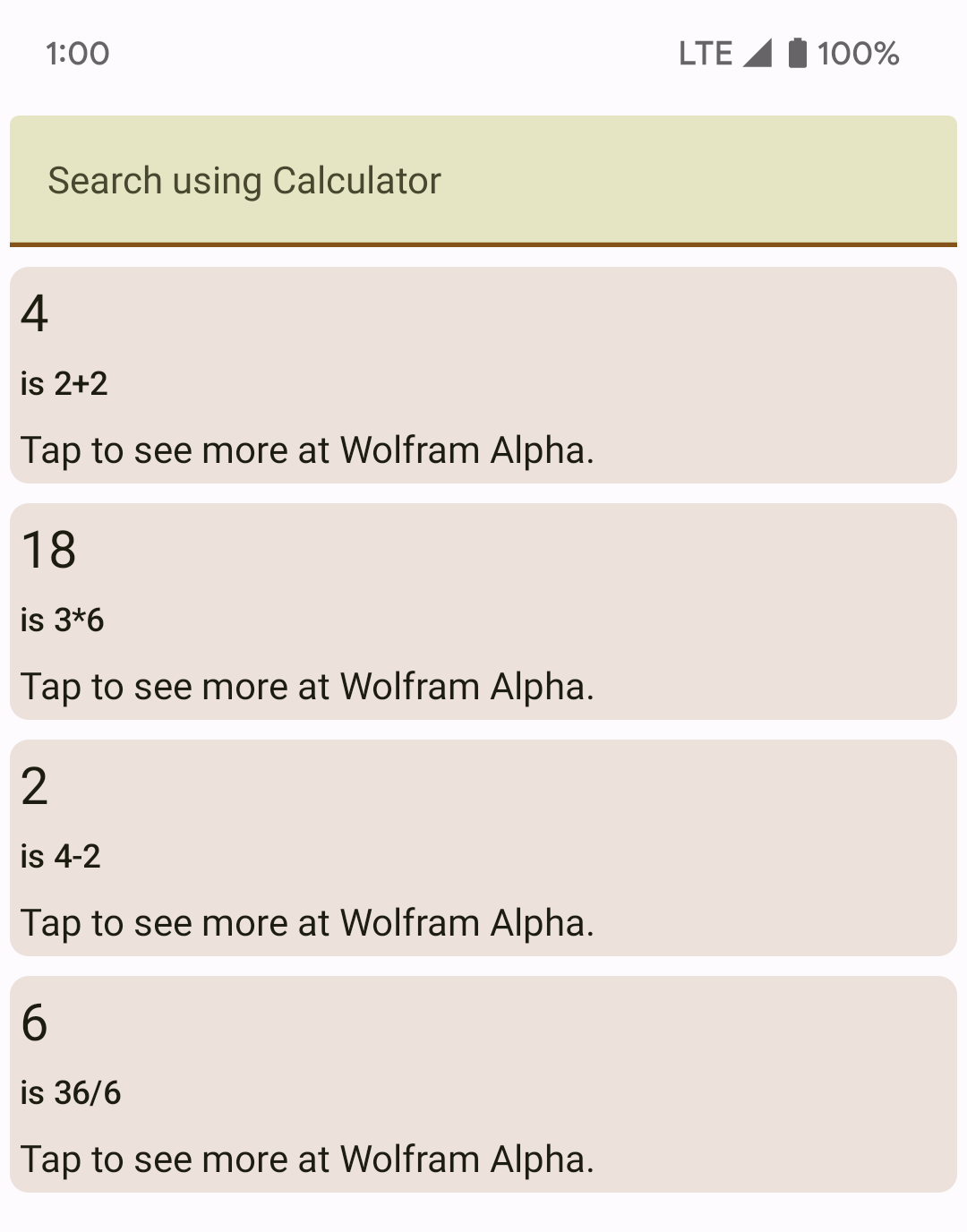
calculatefunction from the last chapter and making a result:val answer = calculate(query) val result = Result( answer.toString(), "Tap to see more at Wolfram Alpha.", "https://www.wolframalpha.com/input?i2d=true&i=" + query.replace("+", "%2B"), "is $query" )The 1st, 2nd and 4th arguments of
Resultindicate the page's name, description (can be empty) and domain. The 3rd argument is the URL to open. In this example the search result will open Wolfram Alpha when tapped.Add that result into the list and pass it to the app:
list.add(result) setResults(list)
And since our SERP provider doesn't make web requests, we can just return null instead of a web request:
return null
At this point your
Calculatorclass should look like this.
- Build and run Gugal. Enter a 2 number calculation in the search bar and you should see the result: